The Dance of Seasons: Understanding How Seasons Change
Nature WorldWide June 19, 2024 0
As the Earth makes its annual journey around the sun, we experience the changing rhythms of the seasons. This cyclic transformation from winter to spring, summer to autumn, and back again is a Natural Phenomenon affecting the environment and our daily lives, cultures, and traditions. But what exactly causes the seasons to change? Let’s explore the science behind this captivating How Seasons Change.
Let us understand in detail How Seasons Change:
The Tilt of the Earth
The primary reason for the changing seasons is the tilt of the Earth’s axis. The Earth is tilted at an angle of about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane around the sun. This tilt remains consistent as the Earth orbits the sun, meaning different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
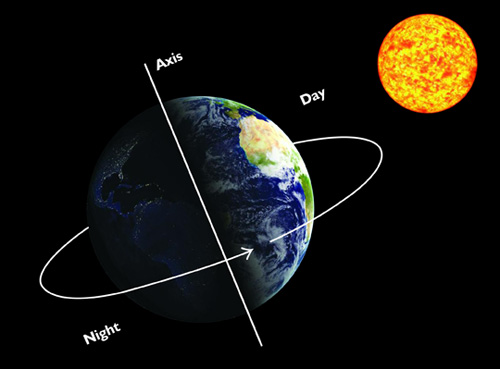
- Summer: When a hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it experiences summer. During this time, the sun’s rays strike the Earth more directly, resulting in longer days, shorter nights, and warmer temperatures.
- Winter: Conversely, when a hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, it experiences winter. The sun’s rays hit at a more oblique angle, leading to shorter days, longer nights, and cooler temperatures.
Read More: Top Unbelievable Natural Things in Scotland
The Earth’s Orbit
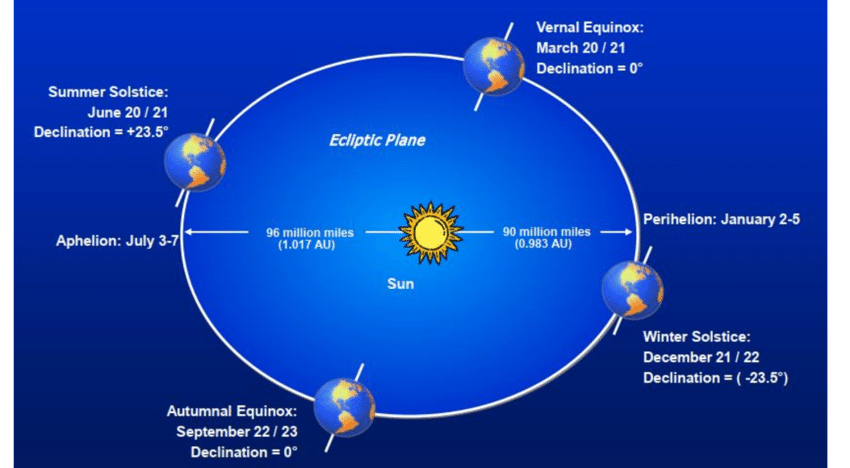
While the tilt of the Earth’s axis is the main driver of seasonal changes, the shape of the Earth’s orbit also plays a role. The Earth follows an elliptical (oval-shaped) orbit around the sun, but this orbit is nearly circular, so the distance from the sun doesn’t significantly affect seasonal temperatures. However, the position of the Earth in this orbit at different times of the year helps determine which hemisphere experiences summer or winter.
Read More: Types Of Forests In The World
Equinoxes and Solstices
The progression of the seasons is marked by four key events: the equinoxes and solstices. These events divide the year into four distinct seasons.

- Spring Equinox: Around March 20th or 21st, the spring equinox occurs. During this time, the sun is directly above the equator, and day and night are approximately equal in length. This marks the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Summer Solstice: Around June 21st or 22nd, the summer solstice occurs. During this time, the Northern Hemisphere tilts most directly towards the sun, resulting in the longest day and shortest night of the year. It marks the start of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Autumn Equinox: Around September 22nd or 23rd, the autumn equinox occurs. Like the spring equinox, day and night are nearly equal. This event heralds the beginning of autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Winter Solstice: Around December 21st or 22nd, the winter solstice occurs. The Northern Hemisphere is tilted furthest away from the sun, leading to the shortest day and longest night of the year. This marks the start of winter in the Northern Hemisphere and summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
Read More: 10 Magnificent Stacks Around the World
Seasonal Changes in the Natural World
The changing seasons bring about profound transformations in the natural world.

- Spring: As temperatures rise and daylight increases, plants grow, flowers bloom, and animals emerge from hibernation. It’s a season of renewal and growth.
- Summer: Warm temperatures and long days create ideal conditions for plant growth and outdoor activities. Many animals are active, raising their young and using abundant food supplies.
- Autumn: As daylight wanes and temperatures drop, plants prepare for winter. Leaves change color and fall, animals gather food for the colder months, and some species migrate to warmer regions.
- Winter: Cold temperatures and shorter days lead to dormancy in many plants and hibernation in some animals. Snow and ice cover the landscape in many regions, creating a serene and quiet environment.
Read More: Top 10 Natural Wonders of the World
Cultural Significance of Seasons
Seasons have a deep cultural significance across the globe. Festivals, holidays, and traditions often align with seasonal changes:

- Spring Festivals: Many cultures celebrate renewal and rebirth with Easter, Holi, and Nowruz festivals.
- Summer Celebrations: Midsummer festivities, beach outings, and agricultural fairs mark the warmth and abundance of summer.
- Autumn Harvests: Thanksgiving, Halloween, and the Mid-Autumn Festival are times to celebrate the harvest and prepare for winter.
- Winter Holidays: Christmas, Hanukkah, and Diwali bring light and warmth during the darkest days of the year, celebrating hope and new beginnings.
Read More: Unbelievable Natural Phenomena: A Glimpse into the World’s Wonders
Conclusion
The changing seasons are a reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature and the intricate balance that sustains life. From the tilt of the Earth’s axis to its orbit around the sun, the mechanics of these changes are a marvel of natural engineering. As we observe the shifting patterns of the seasons, we become attuned to the cycles of life, growth, and renewal that shape our world. Understanding these processes deepens our appreciation for the natural world and highlights the importance of preserving the delicate balance that allows life to thrive.
Embracing How Seasons Change connects us to the planet’s rhythms, reminding us of our place within the vast tapestry of life on Earth.




