14 Interesting Facts About Nature You Should Know

Interesting Facts About Nature
Nature surrounds us with its beauty and complexity, inspiring awe and wonder. From the deepest oceans to the highest mountains, the diversity and resilience of the natural world amaze us daily. Here are 14 interesting facts about nature that will enhance your appreciation for the environment around you.
1. The Amazon Rainforest Produces 20% of the Earth’s Oxygen
The Amazon Rainforest, often referred to as the “Lungs of the Earth,” plays a critical role in absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen. Covering 5.5 million square kilometers, this incredible forest holds an estimated 390 billion individual trees. These trees work together to provide around 20% of the planet’s breathable oxygen.

What’s even more fascinating is the Amazon’s incredible biodiversity. It’s home to millions of species, many of which remain undiscovered. Despite its vital role in maintaining Earth’s climate and biodiversity, deforestation continues to threaten this irreplaceable ecosystem.
Read More: Exploring Intriguing and Unknown Facts about Our Home Planet
2. The Great Barrier Reef Is the Largest Living Structure on Earth
Located off the coast of Queensland, Australia, the Great Barrier Reef stretches over 2,300 kilometers. It’s so vast that it can be seen from space. This living structure consists of thousands of individual coral reefs, which are home to a staggering variety of marine life. Coral polyps, tiny creatures that form the reefs, work in partnership with algae to build this vibrant underwater world.
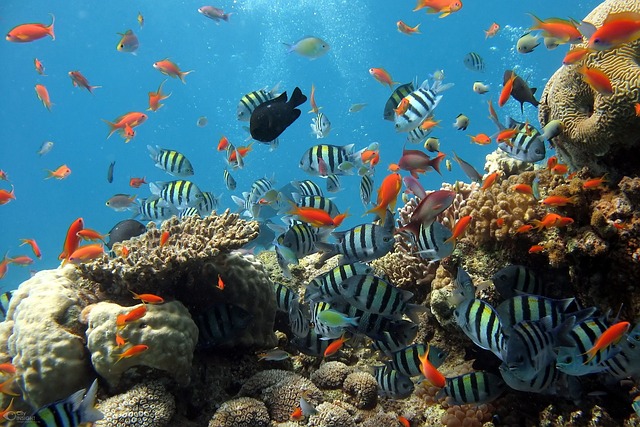

Sadly, climate change and human activities pose significant threats to the reef, with coral bleaching becoming increasingly common. Yet, conservation efforts continue in an attempt to preserve this remarkable natural wonder.
3. Trees Communicate Through a “Wood Wide Web”
Trees don’t stand alone; they communicate through a complex underground network of fungi called mycorrhizal networks. This network allows trees to share nutrients, water, and even warning signals with each other. Older trees, often called “mother trees,” play a pivotal role in distributing nutrients to younger, smaller trees.

Through these connections, trees can help each other survive during times of stress, such as droughts or pest infestations. This fascinating form of communication highlights how truly interconnected life in forests is.
Read More: List Of Top 30 Interesting Facts About Earth
4. Some Plants Can Recognize Their Relatives
Plants may not have brains, but they have surprising capabilities. Some species, like the sea rocket (a coastal plant), can distinguish between sibling plants and strangers. When placed next to a relative, these plants tend to be less competitive for resources like water and nutrients. This behavior suggests plants might exhibit kin recognition, acting more cooperatively toward their family.

Such discoveries challenge our traditional understanding of plant life and suggest that these organisms have more complex social behaviors than previously thought.
5. Octopuses Have Three Hearts and Blue Blood
Octopuses are some of the most intelligent creatures in the ocean, and their anatomy is just as remarkable as their problem-solving abilities. They have three hearts—two pump blood to the gills, while the third pumps it to the rest of the body. Their blood is blue due to the presence of hemocyanin, a copper-based molecule, which is more efficient than iron-based hemoglobin in cold, low-oxygen environments.
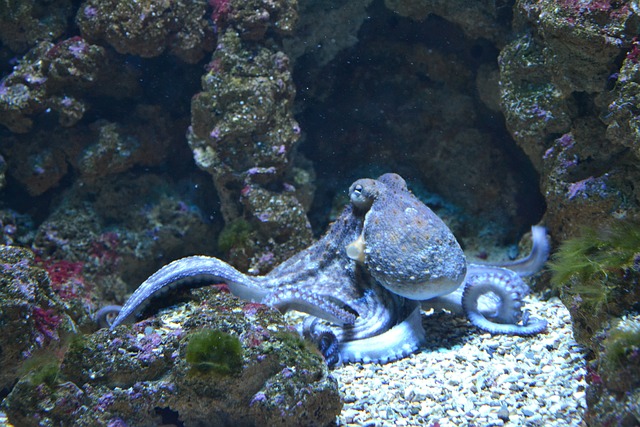

These incredible creatures also possess the ability to camouflage by changing the color and texture of their skin to match their surroundings. Their intelligence, combined with their adaptability, makes them one of nature’s most fascinating species.
Read More: Some Interesting Facts About Earth
6. Water Covers Over 70% of the Earth’s Surface
Water is the essence of life, and it dominates our planet. About 71% of Earth’s surface is covered by water, with the vast majority—97%—residing in the oceans. The remaining 3% exists as freshwater, primarily locked in glaciers and ice caps, leaving less than 1% of accessible freshwater for human consumption.
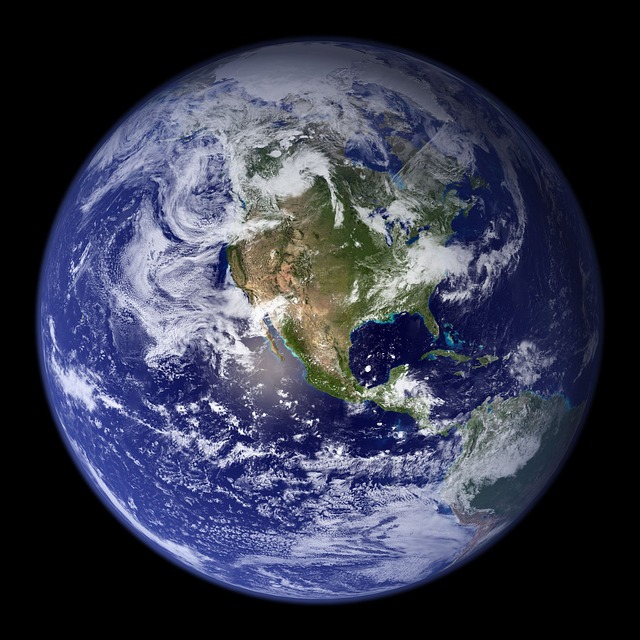

Given how essential water is for all living things, it’s vital that we continue to conserve and protect this precious resource, especially in the face of increasing water scarcity and pollution.
7. Sharks Have Existed Longer Than Trees
Sharks have roamed the Earth for over 400 million years, predating the existence of trees. These ancient predators have survived five mass extinctions and have adapted to changes in climate and ocean chemistry over millennia. Fossil evidence shows that early sharks existed as far back as 420 million years ago, making them older than dinosaurs by about 200 million years.
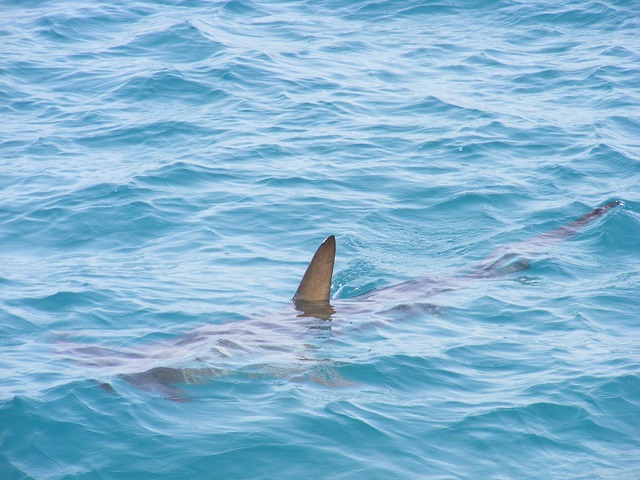

Despite their ancient lineage, sharks face numerous threats today, mainly from overfishing and habitat destruction. Conservation efforts aim to protect these remarkable creatures and ensure their continued survival.
8. The Northern Lights Are a Result of Solar Winds
The mesmerizing display of the Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) occurs when charged particles from the sun, known as solar winds, collide with the Earth’s atmosphere. These particles interact with gases like oxygen and nitrogen, creating vibrant colors that dance across the sky. The green and pink hues most commonly seen are produced when these gases become excited by solar energy.
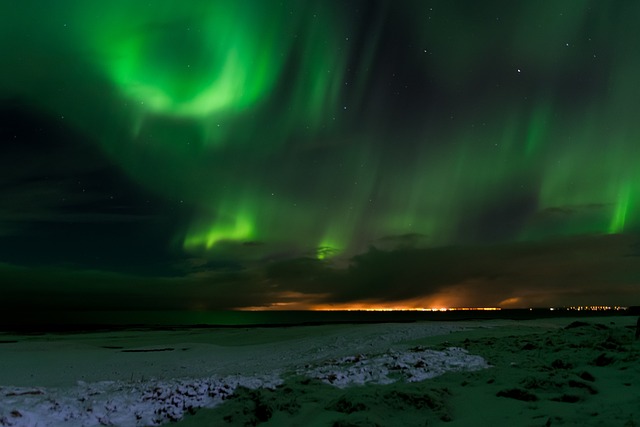

This natural light show occurs near the poles because Earth’s magnetic field directs the charged particles toward these regions. The beauty and mystery of the Northern Lights continue to captivate observers worldwide.
Read More: Discover the World’s Most Naturally Beautiful Countries
9. Ants Have Superhuman Strength
Ants, though small, possess incredible strength relative to their size. Some species can lift objects 50 times their body weight. This strength stems from their unique physiology, which allows them to exert greater force with their muscles due to their small size and exoskeleton structure.
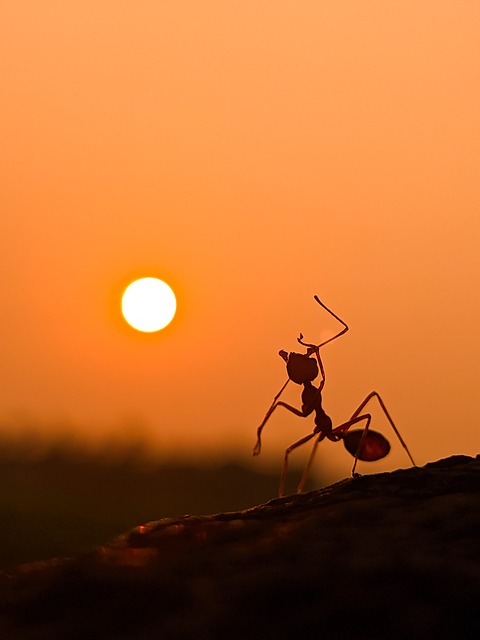

Ants also exhibit complex behaviors, including farming fungi, herding aphids, and communicating through chemical signals known as pheromones. Their social organization and cooperative behavior make them one of the most successful species on the planet.
Read More: 12 Most Amazing Natural Wonders That Exist in India
10. Mount Everest Grows Every Year
Mount Everest, the tallest peak on Earth, stands at 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) above sea level. What many don’t realize is that Everest continues to grow at a rate of about 4 millimeters per year. This growth results from tectonic activity as the Indian and Eurasian plates push against each other, causing the Himalayan Range to rise.
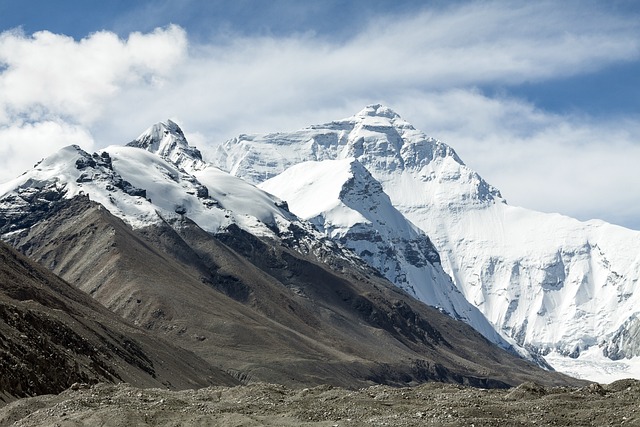

Despite its continued growth, the summit of Everest remains an extreme and dangerous environment, with low oxygen levels, freezing temperatures, and hurricane-force winds challenging even the most seasoned climbers.
11. The Hummingbird Is the Only Bird That Can Fly Backwards
Hummingbirds are marvels of the avian world. These tiny birds, known for their rapid wing beats (up to 80 beats per second), are the only birds capable of flying backward. Their unique ball-and-socket shoulder joints allow them to rotate their wings in all directions, giving them unparalleled maneuverability.
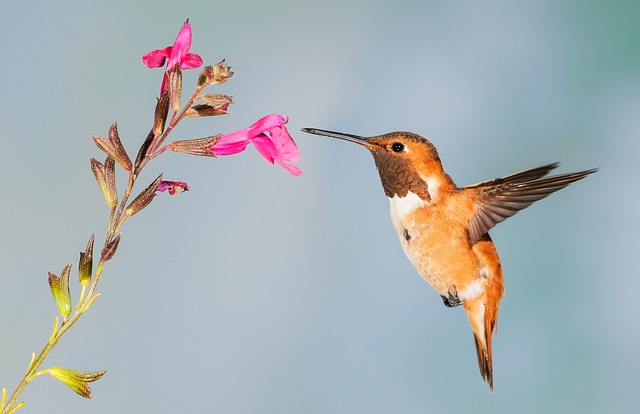

Their high metabolism requires them to consume enormous amounts of energy, feeding on nectar from flowers and small insects to fuel their constant movement. Despite their size, hummingbirds cover vast distances during migration, some traveling up to 2,000 miles.
Read More: Top Amazing Natural Structure in India
12. A Single Tree Can Absorb 48 Pounds of Carbon Dioxide a Year
Trees play a crucial role in combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide, one of the primary greenhouse gases responsible for global warming. On average, a mature tree can absorb around 48 pounds of CO2 per year and release enough oxygen to support two people.

This makes reforestation and tree-planting efforts vital to reducing the impact of carbon emissions. Beyond absorbing CO2, trees provide habitat for wildlife, improve air quality, and offer shade, helping to mitigate the urban heat island effect in cities.
13. Jellyfish Have Existed for Over 500 Million Years
Jellyfish are among the oldest living organisms on Earth, with a history stretching back over 500 million years. These gelatinous creatures predate dinosaurs and have remained relatively unchanged over the millennia. Their simple body structure lacks a brain, heart, or bones, relying instead on a basic nerve net to detect environmental changes.
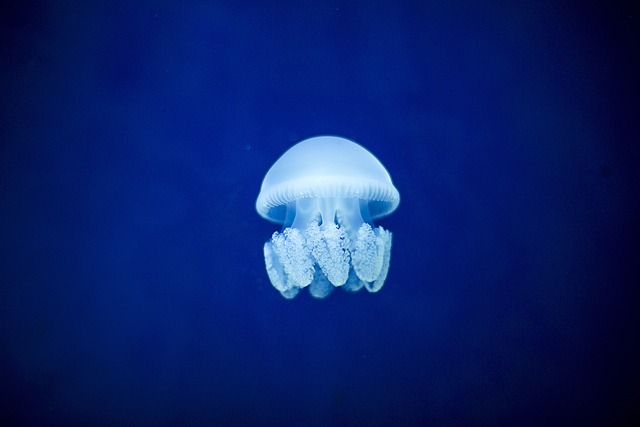

Despite their simplicity, jellyfish play a crucial role in marine ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey. Some species of jellyfish have also attracted scientific attention for their potential to regenerate and reverse aging, offering insights into longevity.
Read More: 11 Most Amazing Natural Wonders in India
14. Earth’s Magnetic Field Protects Us from Solar Radiation
Earth’s Magnetic Field, generated by the movement of molten iron in the planet’s outer core, acts as a protective shield against harmful solar radiation. This magnetic field deflects charged particles from the sun, preventing them from stripping away the atmosphere and causing extensive damage to life on Earth.
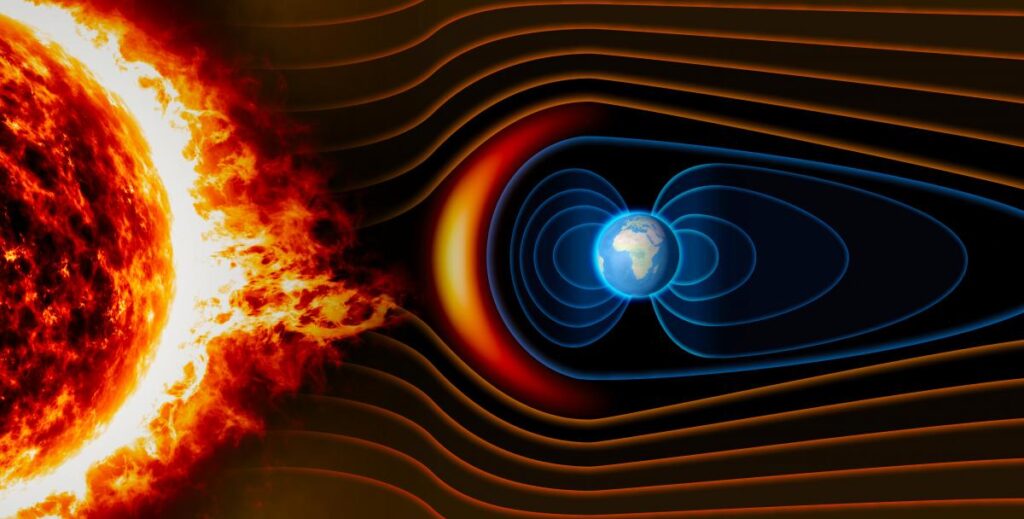
Without this magnetic field, the planet would be bombarded by solar winds, making life as we know it impossible. Interestingly, the magnetic field shifts and even reverses polarity over geological time, a phenomenon known as geomagnetic reversal.
Conclusion
Nature’s complexity, resilience, and beauty never cease to amaze. From the smallest insects to the grandest ecosystems, every element plays a role in maintaining balance on our planet. Understanding and appreciating these fascinating facts about nature helps remind us of our responsibility to protect the natural world. By learning more about the intricacies of nature, we can better contribute to its preservation for future generations.




